| The information on this page refers to License Statistics v6.0 or newer, which introduced the new licensing model (2019). If you are using an earlier version, please refer to the documentation for earlier versions. |
| Info |
|---|
Content of this page is generic and applies to both licensing models supported by License Statistics. This page delivers information on where to look for licensing details. To get familiar with the details about each of the models, read the dedicated documentation page: In order to switch from old licensing model to new one, follow the instructions available on License Transition page. |
License Details page
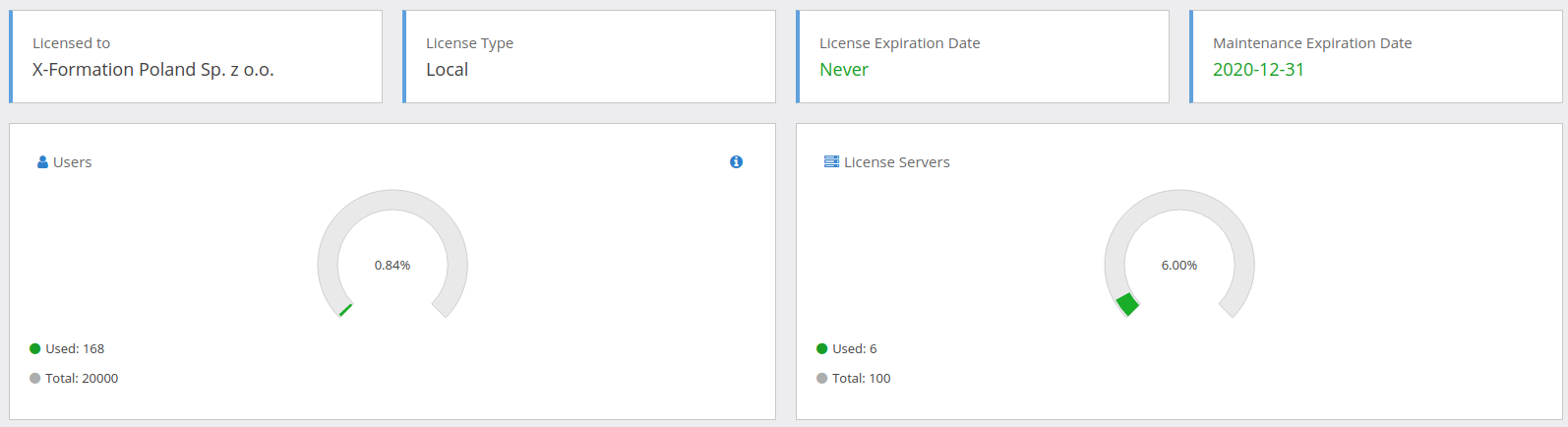
License Statistics has the dedicated License Details page in Administration which delivers all details needed to determine how the license is consumed. It can be accessed by selecting License Details under the Administration menu.
The page contains details about how user and license server licenses are consumed. There is also information about the license limits, type of the license and expiration dates.
| Info |
|---|
For old licensing model (2013) both Realtime and Imported license details are available. In this case there is also panel displaying values needed to switch the licensing to new model (2019). |
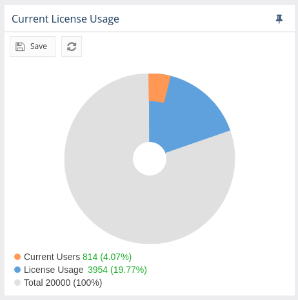
Current License Usage chart
This chart is visible on Current Users report page. In contains number of current users consuming the license in comparison to entire license usage and maximum number of users that license allows for.
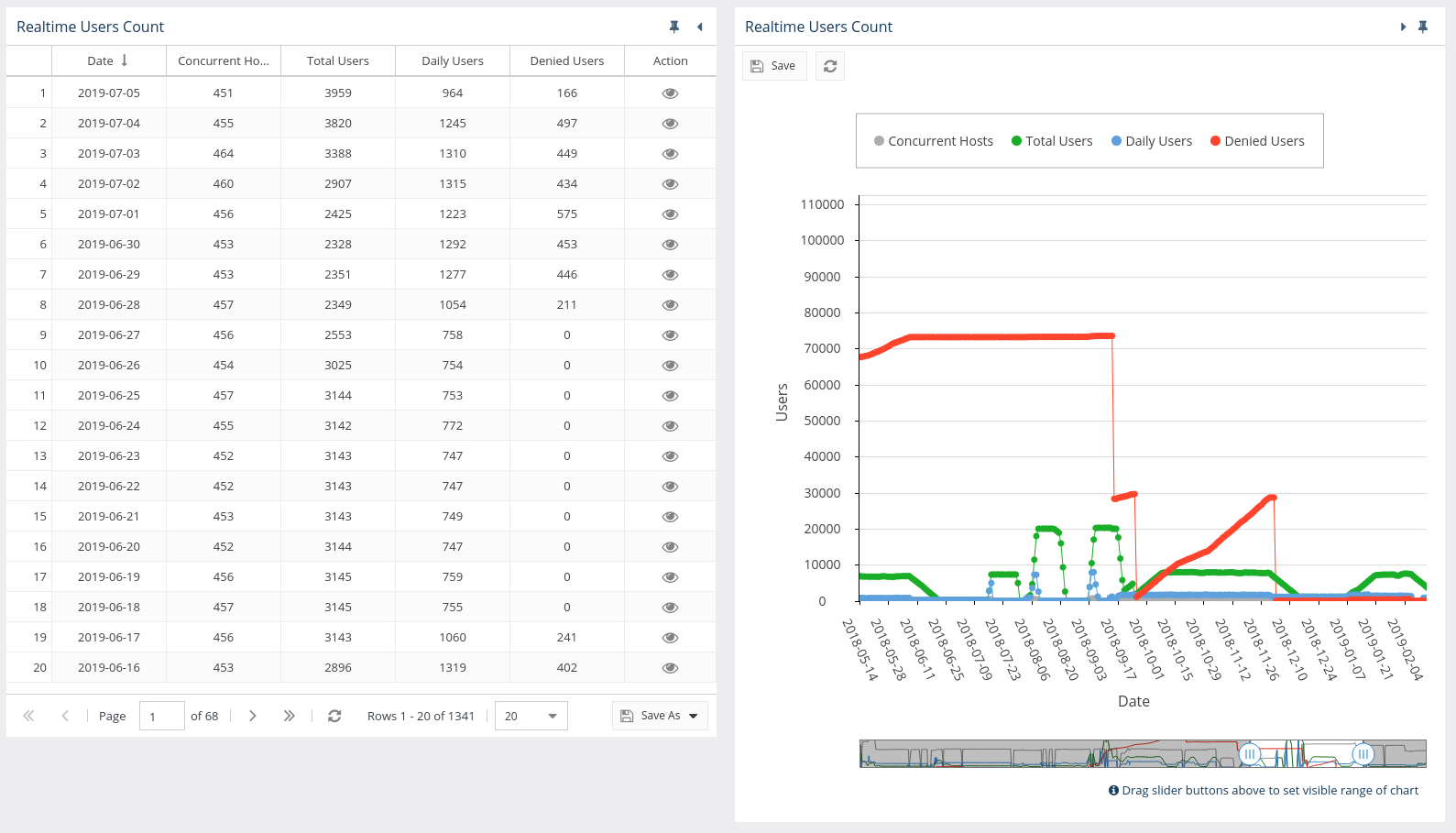
Realtime Users Count report
You can see a
License Statistics considers a "user" to be a unique person or a machine that is accessing the monitored applications. User count is determined as follows:
- The default method of determining user count is based on a) the number of users and b) the number of hosts (machines) the users are running applications from; that is, a unique username/hostname combination. For example, if the user "root" checks out licenses on 100 different hosts, all 100 checkouts will be counted as unique in the Realtime Users Count report (see below).
- An alternative licensing method, available at an additional charge, uses only a unique username and ignores the hostname. Therefore, for the example above, if the user "root" checks out licenses on 100 different hosts, only one user will be counted in the Realtime Users Count report.
Realtime usage
You can see a realtime user count in the Realtime Users Count report, which lists concurrent hosts and daily users on all realtime servers for every day usage is monitored. From this report, you can access a 14-day history of all usernames and hostnames that used monitored licenses for any given date. For example, if you view the 14-day user history for 2015/03/31, you will see the usage details for 2015/03/16 through 2015/03/31. The number of rows in the 14-day history can be used to determine your needs for License Statistics licensing.
Importing of denial logs is licensed under Realtime licensing. All users are counted, regardless of denial date; however, denials will not be counted toward the license limit. Other imported usage is licensed separately, and tracked as detailed below.
See Realtime Users Count report for further information about viewing realtime usage history.
Imported usage
You can review the import log to obtain a user count for imported data. Note the following for imported usage data:
- The total users count includes every user that used a license that is included in the import log, regardless of the date of usage. This differs from realtime user count history, which only counts users who used a license within the past 14 days (as described above).
- The total server count is the number of servers for which data was imported during the past 3 months. Any servers for which data was imported more than 3 months ago are not included in the total server count.
Examples of user count
Users are counted as described in the following examples.
- If User1 runs one application using only HostA, that user is counted as one user.
- If User1 runs two or more applications, still using only HostA, that user is still counted as one user.
- If User1 runs an application from HostA and HostB, either simultaneously or at separate times, User1 is counted as two users.
For applications that use more than one machine (for example, EDA applications), user count is commonly as follows; however, ask your application vendor how their licensing works in such cases.
- If User1 uses his own computer to start EDA_ApplicationA on license servers ServerA and ServerB, thereby consuming a license for User1's computer and for the two servers, this will result in a user count of 3 (User1, ServerA and ServerB are each considered "users" of the application).
...