...
...
functionality that has been removed from License Statistics. Reports have been restructured and reorganized as of License Statistics v6.14. The contents of the Usage Per User report have been moved to Features - History - Usage Per User. |
The Usage Per User report under the Reports section in the left navigation pane shows license usage for a selected type of aggregation, as described below. In this report, you can change time constraints
...
To see a report on the usage of feature, select the Usage Per User tab from the Reports page.
General information
The Usage Per User report lets you monitor license usage for a selected type of aggregation to use for the report (described below). With this report you can change time constraints, as appropriate for your needs; for example, you can display license usage information based on its monthly usage, but limit the displayed results shown to weeks.
It is worth noting that the The Usage Per User report may serve as a warning signal, letting you see the overall trend see whether higher usage is a one-time or a recurring event based on overall trends of license usage based on peak license usage. Therefore, you can consider if the values represent a one-time event or a tendency.
Types of aggregation
You can specify the type of aggregation by which you can aggregate the results for the report. If the aggregation type is not specified, the report will be aggregated by Username and Hostname. Available options are:
...
You can aggregate report results by:
By default, reports are aggregated by Username and Hostname.
| Info |
|---|
| If the User Group and/or Host Group options are disabled, this indicates that no groups have been created. |
How aggregation is applied in a report
Aggregation enables you to specify detailed levels of the produced results. License usage information can be displayed for a specified entity, letting you juxtapose one set of data with another.
| Expand |
|---|
|
The following diagram shows how License Statistics aggregation options are used by real-world entities in a company.
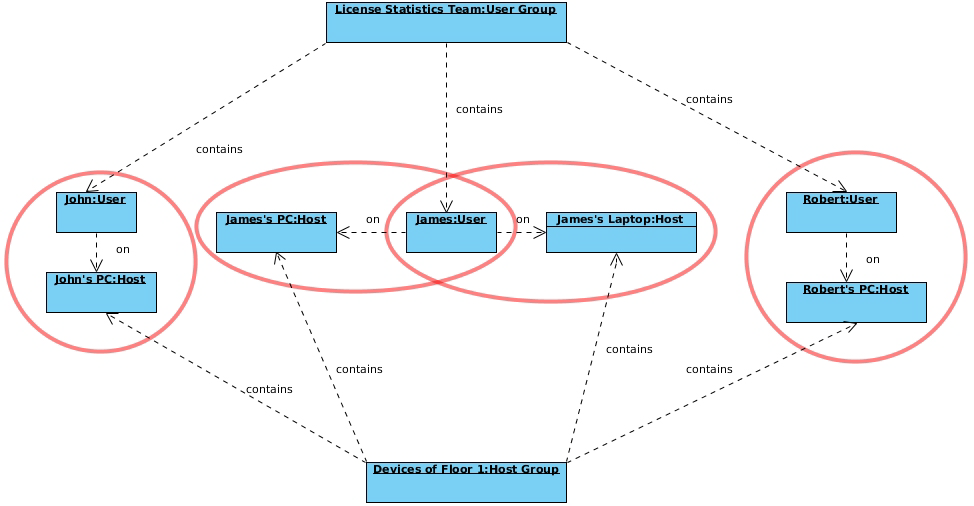 Image Added Image Added
|
 Image Removed
Image Removed
Date Range
The Start Date, End Date, and Time Interval fields are interrelated; e.g., modifying the Start Date field affects the End Date field, depending on the selected Time Interval option. Selecting the "Custom" Time Interval option lets you specify the Start Date and End Date for the report.
...
Types of grouping (time units)
Depending on your needs, you You can group feature usage information by the following units of time:
How grouping by a unit of time works in a report
Grouping by a unit of time lets you group values from specified fields together. For example, license usage information can be collected on a daily basis and grouped into a value for the week, the weekly usage information can be aggregated into a value for the month, and so on.
limited to a month, and within that month displayed based on daily usage. Grouping works in the same way for all other available time units, for any set of selected values.
| Expand |
|---|
|
Let's assume the following values have been returned after grouping feature usage information by |
...
...
...
...
...
When we choose to group the above feature usage information by Month and set the start date to April 4, 2014, we obtain the following values: |
...
When we decide to set the start date to April 1, 2014, we get the following values: |
...
...
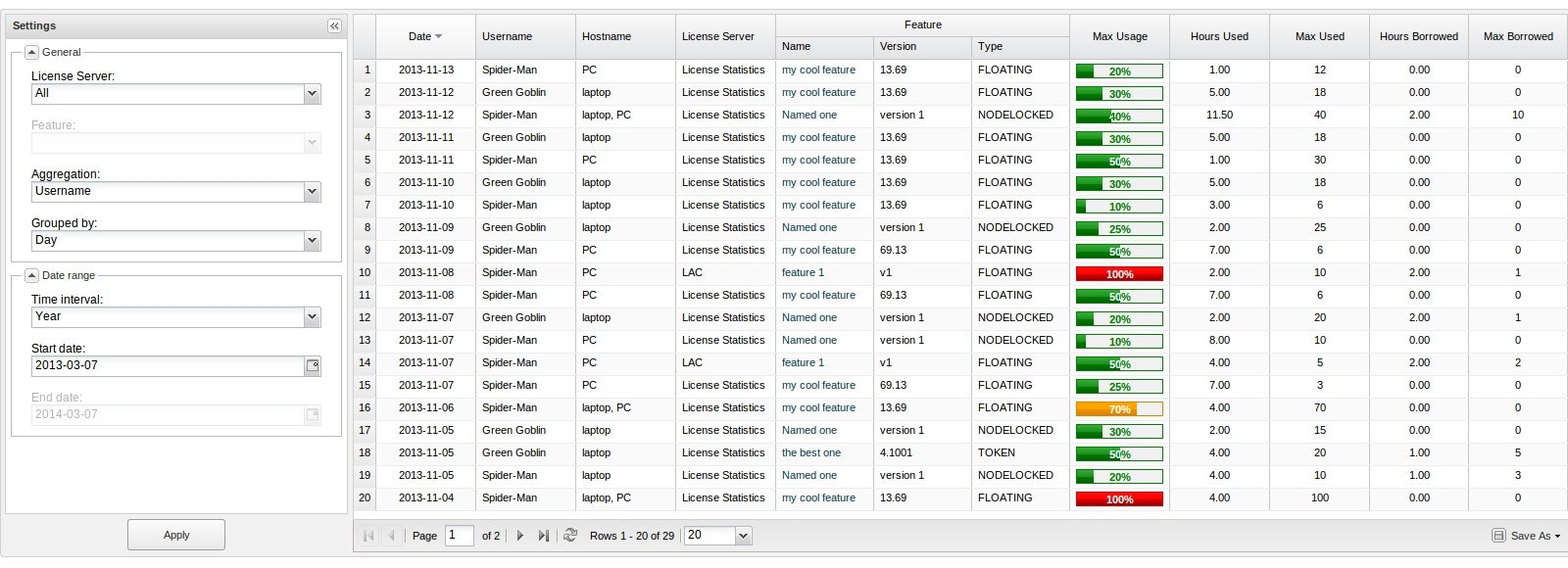 Image Removed
Image Removed
Feature Usage Information
Usage Per User grid
The Usage Per User grid The feature usage information includes the following:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|
| Date | A particular day or period of time, whose format depends on the selected grouping option. Day: YYYY-MM-DD; for example,
|
20142019-04-13. Week: YYYY-MM-DD - YYYY-MM-DD; for example,
|
201311 201311 SundayFriday). Month: YYYY-MM; for example,
|
20142019-04. - Quarter: YYYY-Q[1-4]; for example,
|
2014- 2019-Q2.
- Year: YYYY; for example, 2019.
|
Hostname hostname of | user or a list of users. |
| Host | A single host or a list of |
hostnames | hosts where license usage took place. |
| Username | A single username or a list of usernames. |
Usergroup Name| Host IP | IP address for the host. |
User Group
| The name of a group of users. (This column will be displayed only if aggregating by User Group and one or more user groups exist.)
|
Hostgroup NameHost Group
| The name of a group of hosts |
.| Hours Used | The number of hours at least one license of a particular feature was used and/or borrowed. |
Hours Borrowed | . (This column will be displayed only if aggregating by Host Group and one or more host groups exist.)
|
License server and
feature information | License server name and feature name, version and type. |
| Max Usage | The maximum allowed level of feature usage, expressed in percentages. |
| Hours Used | The sum of hours when licenses of a particular feature were used and/or |
The number of hours at least one license of a particular feature was | borrowed. |
| Max Used | The maximum number of licenses used in a particular time period. |
| Hours Borrowed | The sum of hours when licenses of a particular feature were borrowed. |
| Max Borrowed | The maximum number of licenses borrowed in a particular time period. |
Max Usage | The maximum allowed level of feature usage, expressed in percentages.
| Expand |
|---|
|
To better understand |
...
possible aggregation scenarios |
...
, let’s look at the following example: | Column | Aggregation Type | Scenario |
|---|
| Hours Used/Borrowed |
|
...
| Username | In our example, the results shown in the report are limited by Day. |
|
...
Scenario 1 The user uses 1 license for 8 hours. Calculation: 8 hours = 8 Hours Used |
|
...
...
The user uses 2 licenses for 1 hour, then 10 licenses for 2 hours and 1 license for 2 hours. Calculation: |
|
...
...
...
24 Hours Used | | Max Used/Borrowed |
|
...
| Username | In this example, the results shown in the report are limited by Day. |
|
...
Scenario 1 The user uses 2 licenses |
|
...
in the same time during the day. |
|
...
Calculation: 2 licenses in the same time = 2 Max Used/Borrowed Scenario 2 |
|
...
...
1 license for an hour in the morning and 1 license for an hour in the afternoon.
Calculation: 1 license in the same time = 1 Max Used/Borrowed Scenario 3
The user uses 1 license constantly for the entire day, while the other one is used only for 1 hour.
Calculation: 2 licenses in the same time = 2 Max Used/Borrowed
| | Max Usage |
|
...
| Username | In our example, the number of available licenses for a particular feature is 10. |
|
...
Scenario 1 The user uses 2 licenses throughout the day. |
|
...
Calculation: 2 licenses out of 10 licenses = 20% |
|
...
Scenario 2 The user uses 5 licenses |
|
...
constantly for the entire day, |
|
...
except 1 hour when only 2 licenses are used |
|
...
...
Calculation: 5 licenses out of 10 licenses = 50% |
|
...
Scenario 3 The user uses 3 licenses |
|
...
constantly for the entire day, but |
|
...
additionally 5 licenses are used for |
|
...
2 hours.
Calculation: 8 licenses out of 10 licenses = 80% |
|


