...
Grouping by a unit of time lets you group values from specified fields together, providing a single record of, thereby providing a single record of distinct values for each group.
Example
Let's assume the following values have been returned after grouping feature usage information by Month.
| Date | Hours Used |
|---|---|
| 2014.04.01 | 10 |
| 2014.04.02. | 20 |
| 2014.04.04 | 30 |
| 2014.04.06 | 40 |
When we choose to group the above feature usage information by Month and set the start date to April 4, 2014, we obtain the following values:
| Date | Hours Used |
|---|---|
| 2014.04. | 70 |
When we decide to set the start date to April 1, 2014, we get the following values:
| Date | Hours Used |
|---|---|
| 2014.04. | 100 |
Grouping works in the same way for all other available time units, for any set of selected values.
The minimum value you can group by is Day. As in the case with aggregation values, the values of columns grouped by other available options are calculated based on calculations of values set for Day for a particular aggregation.
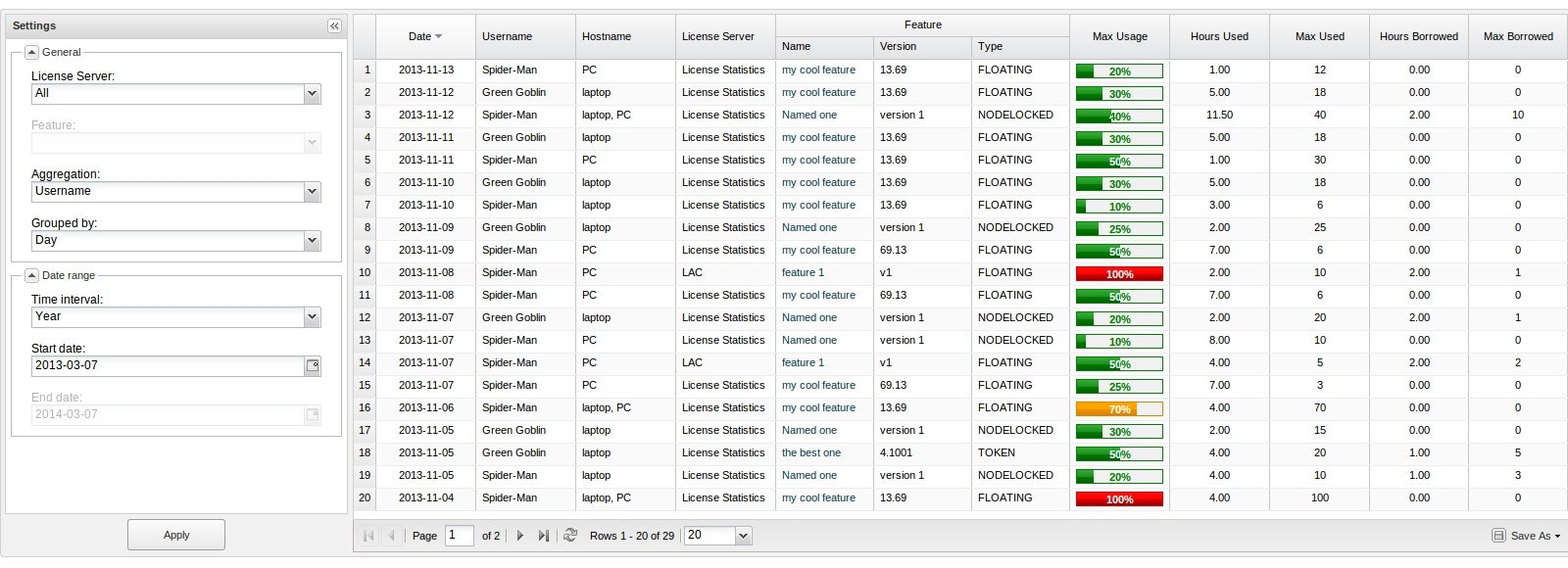
Feature Usage Information
The feature usage information includes the following:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Date | A particular day or period of time, whose format depends on the selected grouping option.
|
| Hours Used | The number of hours at least one license of a particular feature was used and/or borrowed. |
| Hours Borrowed | The number of hours at least one license of a particular feature was used and/or borrowed. |
| Max Used | The maximum number of licenses used in a particular time period. |
| Max Borrowed | The maximum number of licenses borrowed in a particular time period. |
| Max Usage | The maximum level of feature usage, expressed in percentages. |
Example
To better understand how possible aggregation scenarios work, let’s look at the following example:
| Column | Aggregation Type | Scenario | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hours Used/Borrowed | User | In our example, the results shown in the report are limited by Day. Scenario 1 The user uses 1 license for 8 hours. Calculation: 8 hours = 8 Hours Used Scenario 2 The user uses 2 licenses for 1 hour and then 10 licenses for 2 hours and 1 license for 2 hours. | When you choose to use a different aggregation type or when you decide to group by a different value, the sum of the values will be displayed for the following: a). Days in a time frame b). Entities (for example; user, host) in a particular aggregation. |
| Max Used/Borrowed | User | In our example, the results shown in the report are limited by Day. Scenario 1 The user uses 2 licenses in 1 day. Calculation: 2 licenses = 2 Max Used/Borrowed Scenario 2 The user uses 2 licenses in 1 day, but for 1 hour he uses only 1 license Calculation: 2 licenses = 2 Max Used/Borrowed Scenario 3 The user uses 2 licenses in 1 day, but for 1 hour he needs and uses 10 licenses. Calculation: 10 licenses = 10 Max Used/Borrowed | When you choose to use a different aggregation type or when you decide to group by a different value, the highest value will be displayed for the following: a). Days in a time frame b). Entities (for example user, host) in a particular aggregation. |
| Max Usage | User | In our example, the number of available licenses for a particular feature is 10. Scenario 1 The user uses 2 licenses in 1 day. Calculation: 2 licenses out of 10 licenses = 20% Scenario 2 The user uses 5 licenses for 1 day, but for 1 hour he needs and uses only 2 licenses. Calculation: 5 licenses out of 10 licenses = 50% Scenario 3 The user uses 3 licenses in 1 day, but for 1 hour he needs and uses 8 licenses. Calculation: 8 licenses out of 10 licenses = 80% | When you choose to use a different aggregation type or when you decide to group by a different value, the same method of calculation will be applied. It should be noted that the Max Usage value may serve as a warning signal, giving you information about the highest values of feature usage. It is worth considering if the values represent a one-time event or a tendency. |