Excel’s Power Query tool is used to transform and prepare data. Power Query not only lets you import data from a variety of sources, but gives you the ability to transform and use the data to suit your needs. Using Power Query, you can set up a query once, and then reuse the query by “refreshing” the data as often as needed.
Step-by-step instructions for importing License Statistics data directly into Excel using Power Query are detailed below.
- In Excel, click From Web under the Data ribbon to open the Power Query editor.
- In the From Web pane, toggle on Advanced.
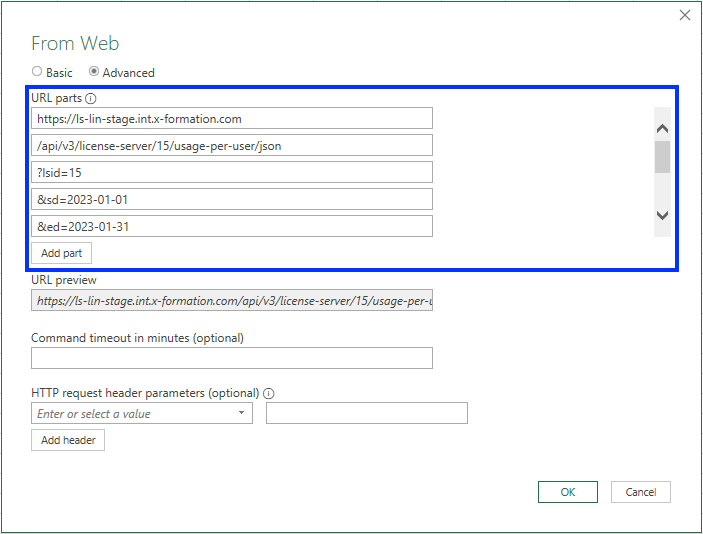
- Under the URL parts area, add lines for the parts as shown in the following table and illustration:
Part type
Example setting
Host
https://ls-lin-stage.int.x-formation.com
API path
/api/v3/license-server/15/usage-per-user/json
Query parameters
- lsid=15
- sd=2023-01-01
- ed=2023-01-31
- grat=DAY
- agrt=USER_HOST
- offset=0
- limit=100
- Under “HTTP request header parameters,” add an X-Auth-token header using a token generated from License Statistics, and click Add header.
- Click OK to continue.
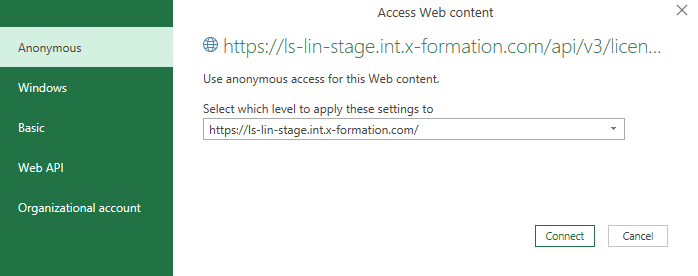
- Choose Anonymous as the web content access type, and click Connect.
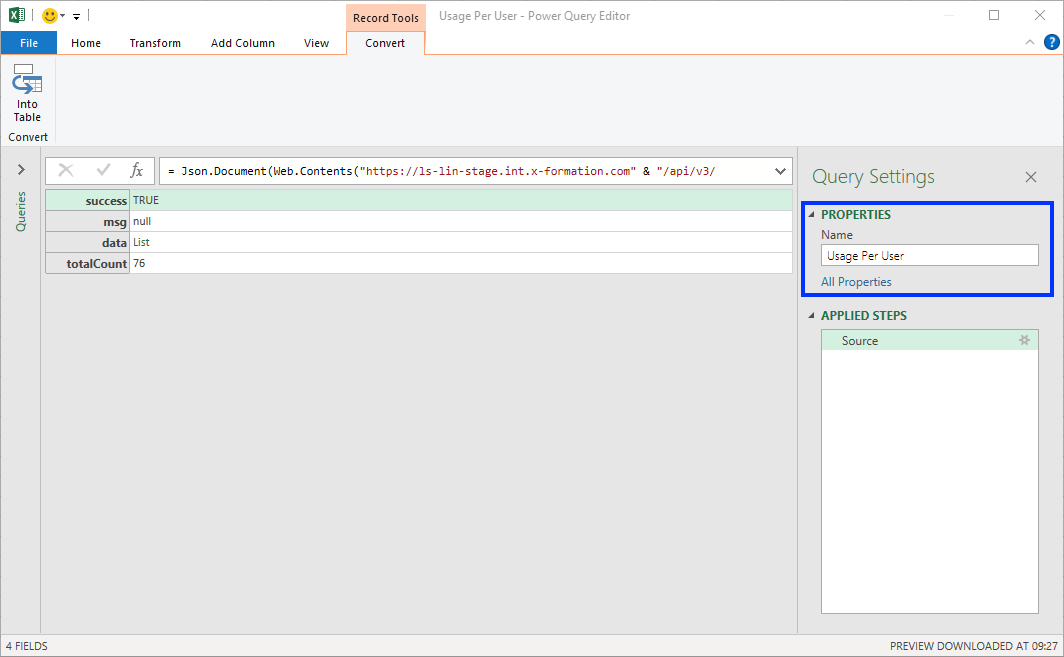
- Click Info Table under the Content ribbon.
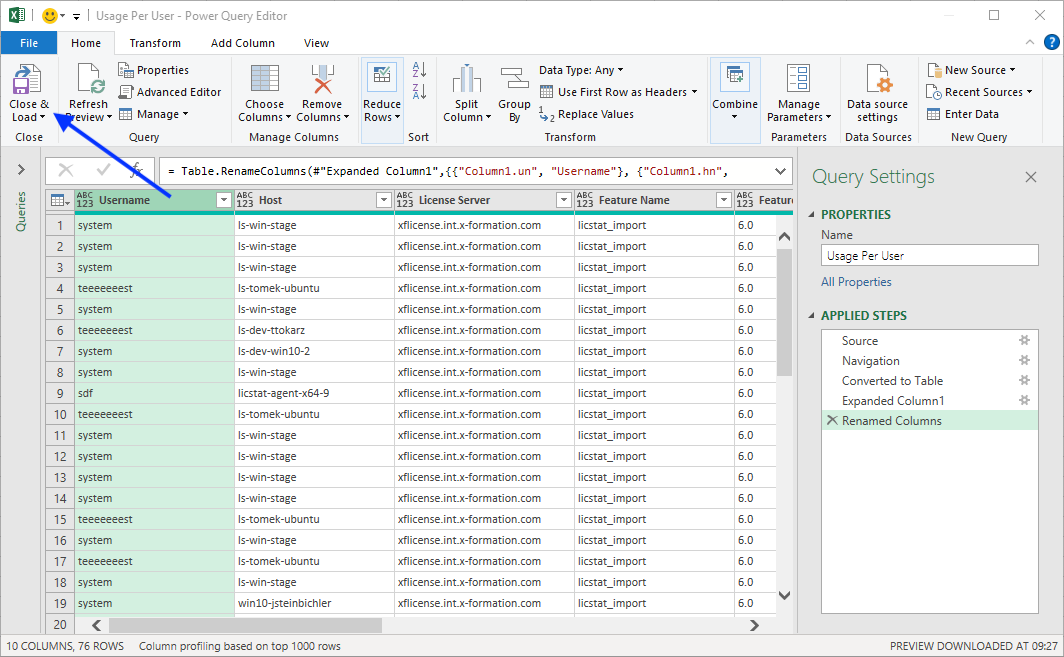
- Optionally, you can name the query using the Properties area under Query Settings. In our example, we named the query “Usage Per User” to indicate the type of data being retrieved.
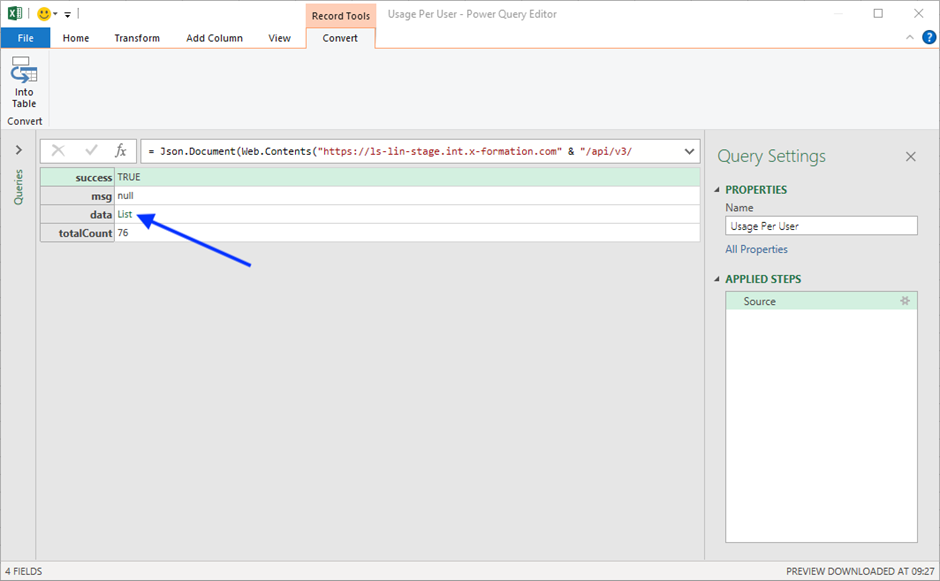
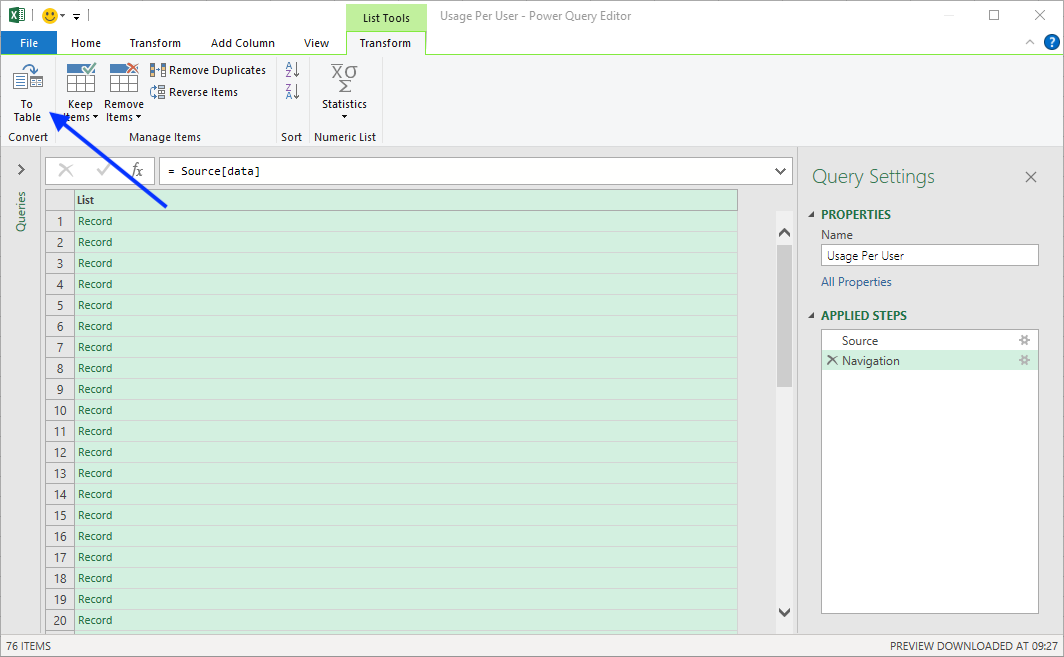
- Select data list from the table.
- Click To Table under the Transform tab to convert the data list to a table.
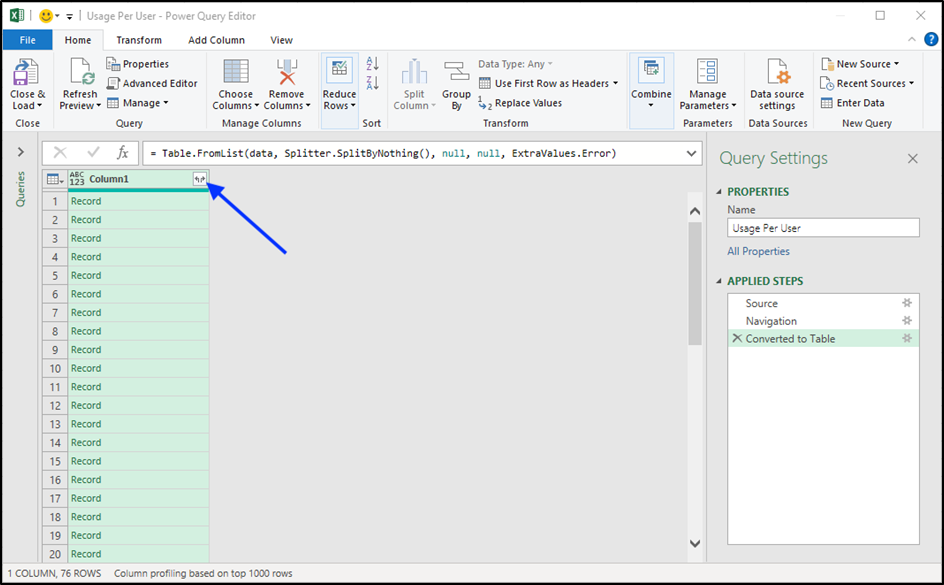
- In the resulting “To Table” pane, choose None as the delimiter, and choose Show as errors to handle extra columns.
- Click OK.
- Click the expand icon in the upper right of the Queries table to expand the table columns.
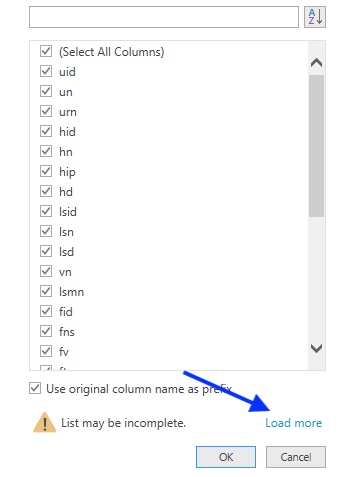
- Click Load more at the bottom of the list to load all the columns.
- Select the columns to include in the query; for example:
- un
- hn
- lsn
- fns
- fv
- massage
- hu
- mu
- ldtc
- ft
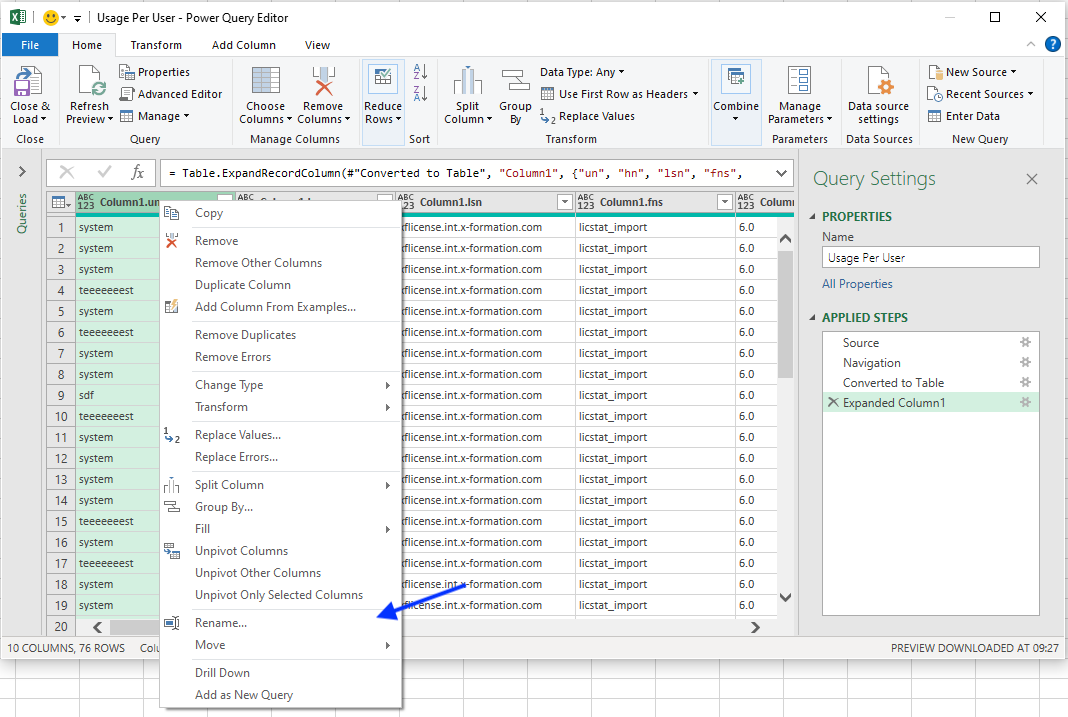
- Optionally, you can rename columns by right-clicking on the column header and choosing Rename from the right-click menu.
For example, you might rename columns to their corresponding label found in License Statistics:- us = Username
- hn = Host
- lsn = License Server
- fns = Feature Name
- fv = Feature Version
- musage = Max Usage
- hu = Hours Used
- mu = Max Used
- ldtc = Denials
- ft = Total
- Click Close & Load.
- If you want to refresh data automatically, perform the following additional steps:
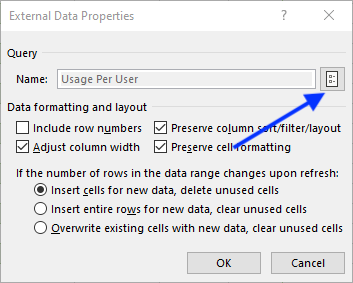
- Go to Queries & Connections under Excel’s Data tab, and select Properties.
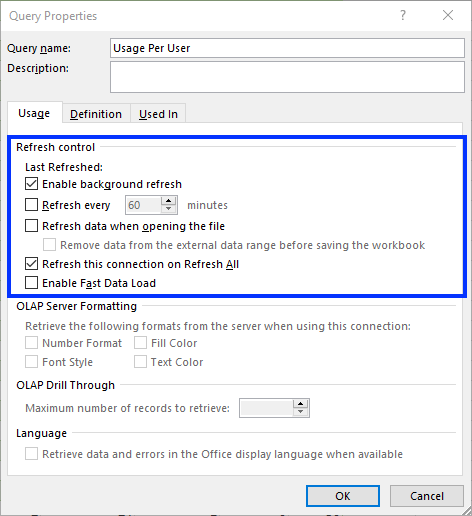
- In the External Data Properties dialog, click Query Properties.
- Under the Usage tab, set the refresh options as desired.
- Go to Queries & Connections under Excel’s Data tab, and select Properties.